BLOW & BLOW:
An expression used to identify the production process of the I.S machine making narrow neck containers. Glass is blown in the blank mould and later blown again in the blow mould.

Blow & Blow Process Mould Equipment
1. Funnel

The funnel has two functions. First it acts as a guide for the gob to enter the blank. Second it provides clearance for the introduction of “settle blow” air into the blank.
2. Baffle

The baffle has two functions. First it provides settle blow air through internal porting in the baffle. Second it seats on top of the blank completing the blank cavity for the formation of the parison.
3. Blank Mould

The blank is the primary piece used to form the parison through the use of settle blow air and counter blow air. It is designed to provide the correct amount of glass wall thickness throughout the finished container.
4. Neck Ring

The neck ring consists of two neckring halves and a guide ring. The guide ring is an internal part and normally forms the top of sealing surface of the finish. The neck ring forms the finish and holds the parison during transfer from the blank to the blow mould. The guide ring is sometimes referred to as guide plate.
5. Thimble

The thimble guides the plunger into the neck ring and creates a seal for counter blow air.
6. Plunger

The plunger forms the inside surface of the finish and provides counter blow during the parison forming process.
7. Mould
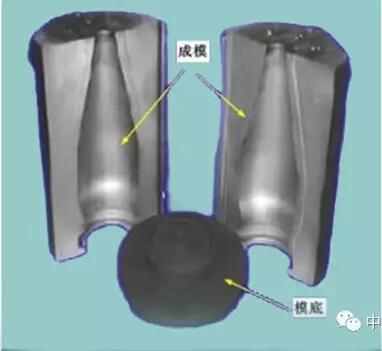
The mould forms the finished container.
8. Bottom Plate

The bottom plate is used in conjunction with the mould to form the finished container. The bottom plate forms the bottom of the container.
9. Blow Head

The blow head sits on top of the mould. It is used to introduce final blow air into the parison blowing it to the shape of the mould.
Glass Container Blow & Blow Process and Its Mould Equipment
Core prompt
:BLOW BLOW:expression used to identify the production principleof the I.S machine making narrow neck containers. glass
- The next article : Wang Yang investigated the Shajiabang glass mould innovation platform
- The up article : 暂无
Click on the list
Recommended Photo
RecommendedNews
- Ardagh Group launches interactive 3D glass packaging experience
- Ardagh Group Launches Development Machine
- Stölzle digitizes their production processes
- Glass Container Neck Narrow Press & Blow Process and its Mould Equipment
- Glass Container Press & Blow Process and its Mould Equipment
- Bormioli Pharma: packaging innovations offer solution to unstable drug formulations
- Innovation from Stoelzle Masnieres Parfumerie for perfumery and cosmetics bottles and jars
- Stoelzle Masnieres Parfumerie presents an innovative decoration process at PCD
- VDV Lubricants: safest and most efficient technology of today and tomorrow
- How Glass is Made
Hot recommended
Products | Buying | Suppliers | News | Exhibitions |
Home
| Contact
| About Us
| Use Agreement
| Copyright Privacy
| Site Map
|
Site Feedback | Advertising Services | REWARDS | 苏ICP备11065233号
©2014 China Glass Mould Network All Rights Reserved
Disclaimer: This website is demonstrated by supply and demand information provided by the enterprises themselves, about the authenticity, accuracy and legitimacy of the enterprises, this site does not undertake any guarantee responsibility.
(Best resolution 1024 * 768, IE6 or higher)
(Best resolution 1024 * 768, IE6 or higher)








